CNG Introduction
CNG stands for Compressed Natural Gas. CNG is a gasoline-based fuel gas. It is a non-toxic and clean-burning gas. It is a mixture of hydrocarbons that mostly consists of methane. Compressed natural gas and liquefied natural gas are the two types of natural gas currently used in vehicles. In this article, we will discuss the history of compressed natural gas, benefits and drawbacks, applications, and future prospects.

So What is CNG?
CNG is a gaseous mixture of hydrocarbons, primarily methane. It is a fuel made up of petrol, which is predominantly composed of methane.
- The name “Compressed Natural Gas” comes from the fact that CNG is compressed to a pressure of 200 to 250 Kg/cm2. It has been reduced to less than one percent of its original volume at standard atmospheric pressure.
- Natural Gas is not a liquid. It is safer than gasoline and diesel.
- It has no color and is lighter than air.
- It is popularly used in vehicles as a fuel, however, vehicles must first be modified.
- CNG is a viable alternative to gasoline, diesel, and LPG.
- Vehicles that are compatible with natural gas produce significantly less pollution.
- CNG is far superior to gasoline because it is both cleaner and more cost-effective.

History of CNG
- In the mid-eighteenth century, experiments with compressed gases began.
- Columbia Natural Gas of Ohio tried a CNG carrier in the 1960s. The ship was supposed to transport compressed natural gas in vertical pressure bottles, but the pressure vessels were too expensive.
- Since the 1930s, automakers in their industries have occasionally employed methane gas.
- Since 2008, the market for CNG and LPG has grown due to increased gasoline prices and the desire to reduce air pollution.
- Following the 1990s, many countries began to adopt CNG fuel in vehicles, as well as its requirements.
- Iran, Pakistan, Argentina, Brazil, and China have the largest number of cars powered by compressed natural gas in the world. By 2011, there were almost 14.8 million natural gas vehicles in use around the globe.
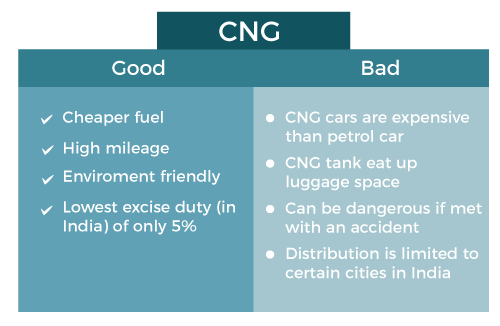
Advantages and Disadvantages of CNG
Compressed natural gas comes with various pros and cons, here we are sharing the Pros and cons of natural gas.
Advantages of CNG
- When burned, compressed natural gas releases a number of pollutants that is far lower than that produced by gasoline or oil.
- CNG emits fewer greenhouse gases and thus has a lower carbon footprint. Reports say that CNG has about 28% fewer greenhouse gas emissions over its entire life cycle than the average gasoline fuel in that market.
- Compared to gasoline and oil, CNG is a more eco-friendly fuel source.
- The primary application of Compressed natural gas is in motor vehicles; consequently, the primary advantage of CNG for motor vehicles is that Natural Gas-powered vehicles have lower costs of maintenance compared to vehicles, which are powered by gasoline or diesel.
- In the event of a leak, the potential damage caused by natural gas is significantly less severe than that caused by other fuels.
- Compared to diesel-powered cars, natural gas vehicles may cut noise by as much as 50 percent, making truck traffic on the street calmer.
- It has low CO2 emissions.
- Natural gas is cheaper when compared to gasoline and it is utilized for transportation, and its benefit is its ability to move large ships over long distances at much lower costs.

Disadvantages of CNG
- Compressed natural gas-powered cars demand more fuel storage space than gasoline-powered vehicles.
- CNG-powered vehicles are not a solution to reducing the carbon footprint when the whole natural gas production, distribution, and vehicle infrastructure are considered.
- The leakage of unburned methane as natural gas is a major problem since methane, the primary component of natural gas is consequently seen as a contributor to global warming.
- The natural gas-powered car has less power output than cars powered by petroleum.
- It has less energy density.

Uses of CNG
- The most popular use of CNG is in motor cars. Not only can a vehicle run solely on natural gas, but it can also function as a bi-fuel, meaning that it can be fueled by a combination of CNG and another fuel.
- It is also used in train operations, as it is cheaper than diesel. Natural Gas is not commonly used in trains. Although some trains are diesel-electric based, they have been transformed into natural gas-operated trains.
- Compressed natural gas is also used in transporting materials via ships. The loaded ships go on short and long trips, proving economical both ways when compared to conventional-based fuels.

So What Will Be the Future of CNG?
In 2011, there were 14.8 million cars powered by natural gas around the globe. Iran, had 4 million automobiles powered by compressed natural gas, while Pakistan had 3 million natural gas-operated vehicles.
- The use of compressed natural gas is growing in South America, Europe, and North America as a direct result of rising oil prices.
- In response to high fuel prices and environmental concerns, CNG has been used in local 3-wheeler transport, heavy-duty trucks, buses, and trains.
CNG is good for the environment in many ways, like putting out less carbon dioxide and a lot less harmful gases than traditional cars. Hence, the usage of CNG as a fuel over traditional fuels is safe and has a good future ahead. Even though it has methane leaks, which cause a lot of trouble like global warming when you look at the whole process, from making it to selling it. As a result, if these challenges are recognized, prioritized, and addressed in an effective and creative manner, it will ultimately be possible for cars of the future to make the full transition to compressed natural gas

Conclusion
In terms of cost-effectiveness and potential difficulties in the future, compressed natural gas is an alternative fuel to conventional fuels. It is being popularly used and its demand is increasing which leads to a conclusion they are much safer and in response to environmental concerns is a better choice
- Also, Read the Article On Energy Consumption in India
- To visit the official website of the Indian Ministry of Power- Click Here
- To visit the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy- Click Here